What is the carbon footprint of water?
The water's carbon footprint means the total greenhouse gas emission caused by our water usage. When water is used to produce goods and services along the entire production chain, this indirect or direct water consumption generates a certain volume of CO2e.
Which water treatment has the largest carbon footprint among all water usage?
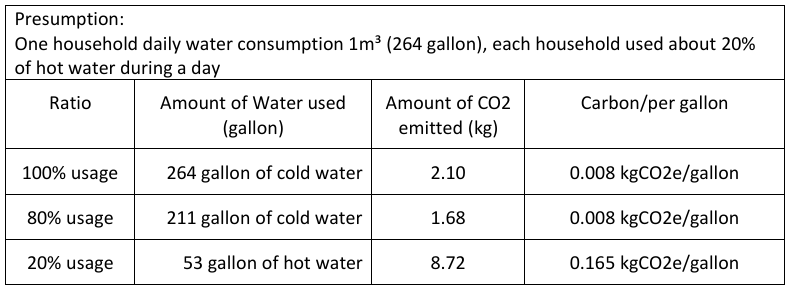
According to the study, water treatment has the highest energy consumption, which could add up to 2 to 3 kg of CO2 per cubic meter in any given water cycle. Among them, the energy used for producing hot water is about 4 times more than using water at a regular temperature.
Since generating hot water requires burning fuels, hot water generation makes up 20 times the greenhouse gas emissions as regular portable water. For example, in a case of 1 cubic meter of a combination of hot water and cold water, the hot water (80%+20%) would emit 10.4 kg CO2e compared to cold water only, which emits about 2.1 kg CO2e.
Information about amount of greenhouse gas emission produced per gallon of water /hot water is excerpt from one of 2022 Greenbuild’s presentation provided by Ibrahim Kronfol/ Senior Mechnical Engineer/ Dar Al Handasah (Shair and Partners).
How does using water efficiently relate to the sustainable SITES rating system and LEED's energy and atmosphere credits?
Since the SITES rating system mainly focuses on the outdoor spaces, "Reducing Outdoor Water Use" (C3.4) will help the project gain the most points (4-6 points). You can apply the following techniques during the establishment period to reduce outdoor water, such as:
using captured rainwater
using reclaimed water
recycling wastewater
recycling grey water
using air-conditioner condensation
(Of course, you can also plant drought-resistant xeriscaping, but that is considered as using the vegetation to minimize building energy use, which is under section 4: Soil + Vegetation.)
The LEED rating system, on the other hand, emphasizes the resilient and sustainable performance of a building. While water usage has no direct correlation to energy usage, processing water consumes energy and emits CO2. These water processes within a building include steps such as pumping water, using a water boiler, or integrating reclaimed water treatment as part of the building system. This water usage will reflect on the building's overall utility bill and be factored into the overall energy performance.
What can we do to reduce CO2 emissions due to our water usage?
Reduce and control the demand,
Seal and prevent the leakage
Digital transformation for water utilities.
Use new technology. (to monitor and control the water usage)
How does your water commissioning plan relate to the ESG report?
ESG reporting categorizes and classifies an organization's greenhouse gas emissions into scope 1, 2, and 3.
Scope 1 means direct emission. That being said, the CO2 emitted during the building operation, such as burning fuels for hot water, is considered within this scope. (Burn)
Scope 2 is indirect energy emission. It is the emission generated during the electric operation process, such as the energy needed to distribute, convey, or treat. (Buy)
Scope 3 encompasses emissions throughout the value chain. It is the emission encompassing all other indirect emissions accumulated during the value chain process, such as end-of-life water collection, wastewater treatment, or wastewater discharge, etc. (Beyond)
By the way...
When talking about water-consumption, water-efficiency and water-reuse, it is inevitable to talk about “water stress” So, what is the "water stress", and how can we avoid it?
Water stress happens when the demand for safe portable water exceeds the available supply in a given area. We generally take these three approaches to prevent such stress from happening.
From the end user: control water usage for end users and integrate grey water and non-potable water in a water processing system.
From the utility line: reduce water leakage within the network and work on smart technology to cut unnecessary water consumption.
Find opportunities from non-portable water: collecting rainwater, treating grey water, and using reclaimed water, etc, to contribute to net positive water use in the local shed.
If you are the first time learn about ESG reporting, here is a little introduction about ESG.
What is ESG? It is a set of criteria used to evaluate a company's commitment to sustainable operation and its impact on our society.
E stands for Environmental factors: events such as energy consumption, water usage, greenhouse gas emission, and overall carbon footprint are considered environmental factors.
S stands for Social: affairs among the company's treatment of employees, supply chain workers, customers, community members, and other groups. Or policies such as fair pay and living wages, DEI (diversity, equity, inclusion) program, workplace safety, responsible sourcing, community engagement, and charitable donation are all considered part of social factor.
G stands for Governance: activities such as internal management, practice, policy, and control, competence of the senior board of directors, financial transparency, risk management, data privacy, ethical business practice, etc, are all considered as part of governance factors.